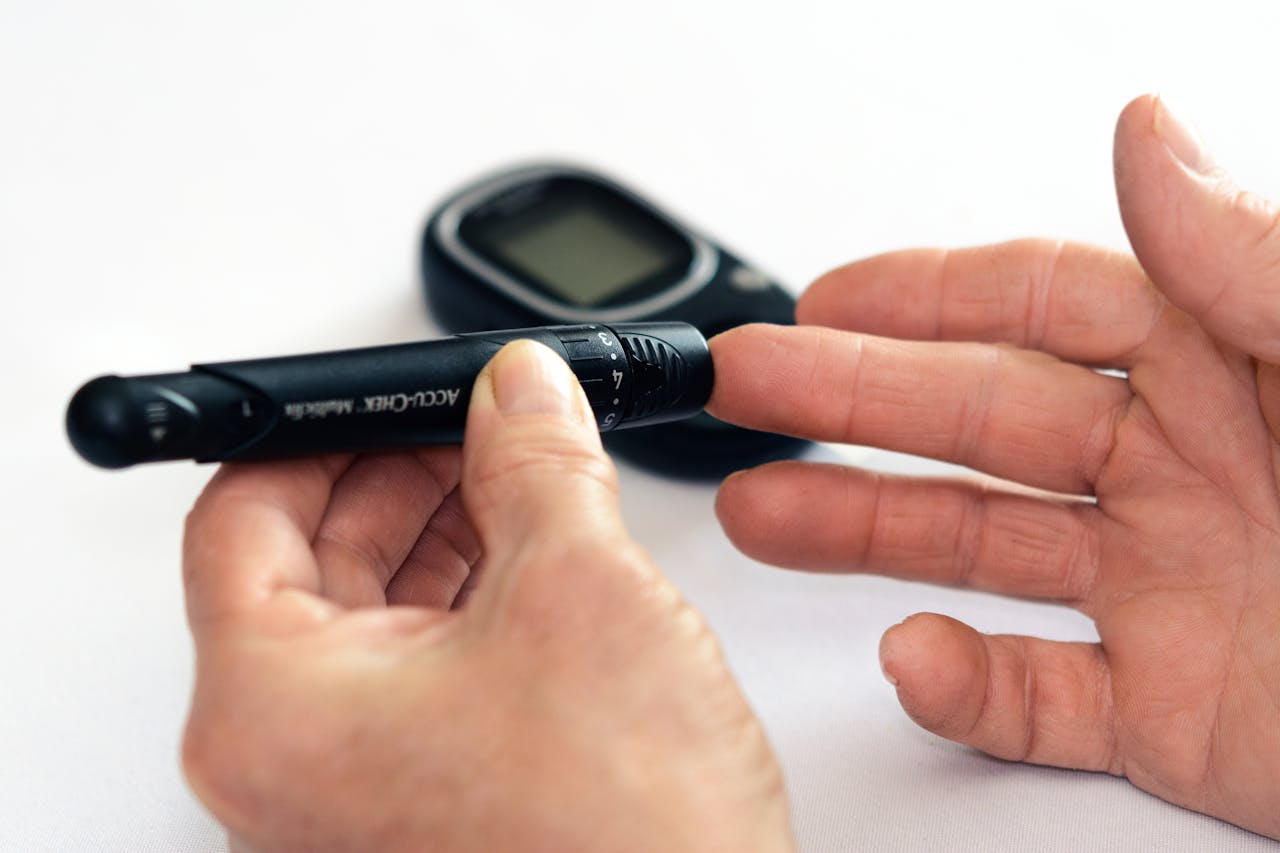
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Over time, it can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. However, with the right dietary and lifestyle changes, managing type 2 diabetes is not only possible but can also greatly improve quality of life. As a clinical nutritionist, my approach focuses on empowering individuals to take control of their condition through informed nutrition and lifestyle choices.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, the body either becomes resistant to insulin—the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar—or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. This results in elevated blood sugar levels, which can damage various organs and tissues over time.
The primary goals of managing type 2 diabetes are:
- Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels
- Preventing complications
- Improving overall health and well-being
The Role of Nutrition in Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing type 2 diabetes. The right foods can help stabilise blood sugar levels, manage weight, and reduce the risk of complications. Here’s how:
1. Emphasising Low Glycemic Index (GI) Foods
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood glucose levels. Foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar.
Low GI foods include:
- Non-starchy vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, peppers, and leafy greens
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, barley, and oats
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Fruits: Apples, berries, and pears
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help maintain more stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of blood sugar spikes.

2. Balancing Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. However, they are also an essential part of a balanced diet. The key is to choose the right types and amounts of carbohydrates.
Tips for managing carbohydrate intake:
- Monitor portions: Be mindful of portion sizes, especially with starchy foods like bread, pasta, and potatoes.
- Pair with protein and healthy fats: Combining carbohydrates with protein or healthy fats can slow digestion and prevent rapid increases in blood sugar.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed carbohydrates: Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provide essential nutrients and fiber that support overall health and blood sugar control.
3. Prioritising Fiber-Rich Foods
Dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes. Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar and helps regulate blood sugar levels. It also promotes a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management.
High-fiber foods include:
- Vegetables: Brussels sprouts, carrots, and artichokes
- Fruits: Berries, oranges, and apples
- Whole grains: Oats, barley, and whole wheat
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas
Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day to support healthy blood sugar levels.
4. Incorporating Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are essential for overall health and can help manage blood sugar levels. They also provide a steady source of energy without causing spikes in blood sugar.
Sources of healthy fats include:
- Monounsaturated fats: Olive oil, avocados, and nuts
- Polyunsaturated fats: Fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts
However, it’s important to limit saturated fats (found in red meat and full-fat dairy products) and avoid trans fats (found in many fried and processed foods), as these can increase the risk of heart disease.
5. Managing Portion Sizes and Meal Timing
Consistent portion sizes and regular meal timing can help maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. Skipping meals or eating large portions can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar, making it harder to manage diabetes.
Practical tips:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals: This can help prevent large spikes in blood sugar.
- Monitor portions: Use measuring tools or visual cues to keep portion sizes in check.
- Plan meals and snacks: Consistent timing can help regulate blood sugar levels.
6. Hydration and Blood Sugar Control
Staying well-hydrated is important for everyone, but it’s especially crucial for those with type 2 diabetes. Dehydration can lead to higher blood sugar levels. Water is the best choice for hydration, as sugary drinks can cause rapid increases in blood glucose.
Tips for hydration:
- Drink water throughout the day: Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Avoid sugary drinks: Limit consumption of sodas, sweetened teas, and fruit juices.
- Incorporate herbal teas: These can be a flavorful, hydrating option without added sugars.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Diabetes Management
Beyond diet, several lifestyle factors contribute to managing type 2 diabetes effectively.
1. Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. It also aids in weight management and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Recommended activities:
- Aerobic exercise: Brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Strength training: Incorporate resistance exercises, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, at least two days per week.
2. Weight Management
For many people with type 2 diabetes, losing excess weight can significantly improve blood sugar control. Even modest weight loss (5-10% of body weight) can have a positive impact.
Strategies for weight management:
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods: Choose foods that provide essential nutrients without excessive calories.
- Monitor progress: Keep track of your weight, food intake, and physical activity to stay on course.
- Seek support: Working with a clinical nutritionist or a weight management program can provide the guidance and motivation needed to achieve your goals.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress can increase blood sugar levels and make diabetes management more challenging. Incorporating stress-reducing activities into your daily routine can help.
Stress management techniques:
- Mindfulness and meditation: These practices can help reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
- Deep breathing exercises: Simple breathing techniques can help calm the nervous system.
- Physical activity: Exercise is a natural stress reliever and can help manage blood sugar levels.
4. Regular Monitoring and Medical Care
Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing type 2 diabetes. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, including blood tests like HbA1c, can help track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your management plan.
Personalised Nutrition Plans
Every individual with type 2 diabetes is unique, and a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work. As a clinical nutritionist, I collaborate with clients to develop personalised nutrition plans that take into account their specific health needs, preferences, and lifestyle. Regular monitoring and adjustments ensure that the plan remains effective over time.
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes is a lifelong commitment, but with the right approach, it can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life. By focusing on a balanced diet rich in low GI foods, fiber, and healthy fats, while managing portion sizes and staying active, individuals can maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. For personalised support and guidance, consulting with a clinical nutritionist can provide the tools needed to successfully manage type 2 diabetes and improve overall health.